Hey there! Are you wondering about the best practices for securing your Wi-Fi network to prevent hackers from getting into your smart security devices? Well, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we will be discussing some friendly and effective tips on how to ensure the safety and security of your Wi-Fi network and smart security devices. So, sit back, relax, and get ready to learn more about how to keep your devices safe from hackers.
Curious to know the steps you can take to safeguard your Wi-Fi network and prevent potential hacking of your smart security devices? From changing your default Wi-Fi network name and password to setting up strong encryption, we will delve into various techniques to enhance the security of your network. Additionally, we will explore the importance of regularly updating your devices and routers, as well as the significance of enabling two-factor authentication for an extra layer of protection. So, whether you’re a tech-savvy individual or just starting to explore the world of smart security devices, this article will provide you with valuable information to ensure the safety and protection of your Wi-Fi network. Stay tuned!
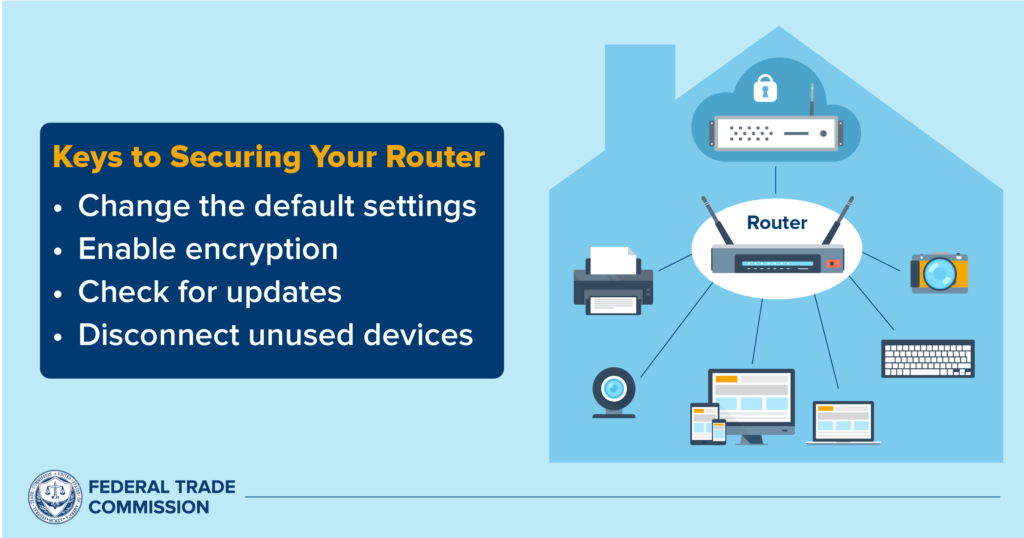
This image is property of consumer.ftc.gov.
Understanding the Importance of Securing Your Wi-Fi Network
In today’s digital age, securing your Wi-Fi network has become more crucial than ever. With the rise of smart security devices, such as security cameras, doorbell cameras, and smart locks, it is essential to protect your network from potential risks and hackers. This article will outline the best practices for securing your Wi-Fi network to prevent hacking of smart security devices.
The potential risks of not securing your Wi-Fi network
Leaving your Wi-Fi network unsecured puts you at risk of various security threats. Hackers can easily exploit vulnerabilities in your network and gain unauthorized access to your smart security devices. This intrusion could lead to serious consequences, including theft, privacy breaches, and even physical harm. By securing your Wi-Fi network, you can significantly reduce the chances of falling victim to such attacks and protect your home and loved ones.
Why securing your Wi-Fi network is crucial for protecting smart security devices
Smart security devices are designed to enhance home security and provide peace of mind. However, without adequate Wi-Fi network security, these devices can become a weak link in your security system. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in your unsecured network to gain access to your devices, disable them, or manipulate their settings. By securing your Wi-Fi network, you can ensure that your smart security devices function as intended and provide the level of protection you expect.
Choosing a Strong Wi-Fi Password
The characteristics of a strong Wi-Fi password
Having a strong Wi-Fi password is the first line of defense against unauthorized access to your network. A strong password should have the following characteristics:
- Length: It should be at least 12 characters long to make it difficult to crack.
- Complexity: It should include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Uniqueness: It should not be a commonly used password or one that has been used before.
- Randomness: Avoid using easily guessable information such as your name, birthdate, or address.
Steps to create a strong Wi-Fi password
To create a strong Wi-Fi password, follow these steps:
- Start with a passphrase: Use a memorable phrase or sentence as the base of your password.
- Manipulate the passphrase: Replace certain letters with numbers or special characters, and mix uppercase and lowercase letters.
- Add complexity: Include a combination of numbers, special characters, and punctuation marks.
- Test the strength: Use a password strength checker to ensure your password is strong and not easily guessable.
- Write it down: Store your password in a secure location, such as a password manager, to avoid forgetting it.
The importance of regularly updating your Wi-Fi password
While creating a strong Wi-Fi password is important, it is equally essential to regularly update it. Regular password changes ensure that even if someone does get access to your password, their access will be temporary. Set a reminder to change your Wi-Fi password every few months or sooner if you suspect a breach or unauthorized access to your network.
Enabling Network Encryption
The role of network encryption in securing Wi-Fi networks
Network encryption plays a crucial role in securing your Wi-Fi network by encoding the data transmitted between your devices and the router. This encryption prevents hackers from intercepting and accessing your sensitive information, such as login credentials and personal data. Without network encryption, your data is vulnerable to eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
Different types of network encryption protocols
There are several network encryption protocols available for securing Wi-Fi networks. The two most commonly used protocols are:
- WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2): This is the most secure and widely used encryption protocol. It employs strong encryption algorithms to protect your data.
- WPA3 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 3): This is the latest encryption protocol and offers enhanced security features compared to WPA2. It provides more robust protection against brute-force attacks and offers individualized data encryption for each connected device.
How to enable network encryption on your Wi-Fi router
To enable network encryption on your Wi-Fi router, follow these steps:
- Access your router’s settings: Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar. This will typically be something like “192.168.1.1” or “192.168.0.1.” Consult your router’s user manual for the exact IP address.
- Enter login credentials: Enter the username and password for your router. If you have not changed these from the default settings, consult your router’s manual or the manufacturer’s website to find the default credentials.
- Navigate to the wireless settings: Look for the wireless settings or security settings section in the router’s settings interface.
- Choose the encryption protocol: Select WPA2 or WPA3 as the encryption protocol.
- Set a strong password: Create a strong Wi-Fi password as discussed earlier.
- Save the settings: Save the changes and restart your router if necessary.
By enabling network encryption and using the latest encryption protocols, you can significantly enhance the security of your Wi-Fi network and protect your smart security devices.
Disabling Remote Management
The risks of leaving remote management enabled
Many Wi-Fi routers come with remote management capabilities, allowing you to access and manage your router’s settings remotely. While this feature provides convenience, leaving remote management enabled can expose your network to potential security risks. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in remote management protocols to gain unauthorized access to your router’s settings and wreak havoc on your network.
Steps to disable remote management on your Wi-Fi router
To disable remote management on your Wi-Fi router, follow these steps:
- Access your router’s settings: Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar.
- Enter login credentials: Enter the username and password for your router.
- Navigate to the remote management settings: Look for the remote management or administration settings section in the router’s settings interface.
- Disable remote management: Find the option to disable remote management and turn it off.
- Save the settings: Save the changes and restart your router if necessary.
By disabling remote management, you eliminate a potential entry point for hackers and reinforce the security of your Wi-Fi network.

This image is property of cdn.comparitech.com.
Changing the Default Network Name (SSID)
Why changing the default network name is important
When you purchase a new Wi-Fi router, it often comes with a default network name, also known as the Service Set Identifier (SSID). Leaving the default SSID unchanged makes it easier for hackers to identify the type of router you are using and target potential vulnerabilities specific to that router model. Changing the default network name adds another layer of security by making it more difficult for hackers to determine the type of router you have.
How to change the SSID of your Wi-Fi network
To change the SSID of your Wi-Fi network, follow these steps:
- Access your router’s settings: Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar.
- Enter login credentials: Enter the username and password for your router.
- Navigate to the wireless settings: Look for the wireless settings section in the router’s settings interface.
- Find the SSID option: Locate the option to change the SSID or network name.
- Choose a new SSID: Enter a unique and meaningful name for your Wi-Fi network.
- Save the settings: Save the changes and restart your router if necessary.
By changing the default network name, you add an extra layer of security to your Wi-Fi network and make it more challenging for hackers to target your specific router.
Implementing MAC Address Filtering
What MAC address filtering is and how it works
Media Access Control (MAC) address filtering is a security feature that allows you to control which devices can connect to your Wi-Fi network. Each device has a unique MAC address that can be used to create a list of authorized devices. By implementing MAC address filtering, you can prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to your network, even if they have the correct Wi-Fi password.
Steps to configure MAC address filtering on your Wi-Fi router
To configure MAC address filtering on your Wi-Fi router, follow these steps:
- Access your router’s settings: Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar.
- Enter login credentials: Enter the username and password for your router.
- Navigate to the MAC address filtering settings: Look for the MAC address filtering or access control settings section in the router’s settings interface.
- Enable MAC address filtering: Turn on MAC address filtering.
- Add authorized devices: Find the option to add authorized devices and enter the MAC addresses of the devices you want to allow on your network.
- Save the settings: Save the changes and restart your router if necessary.
By implementing MAC address filtering, you enhance the security of your Wi-Fi network by restricting access to authorized devices only.

This image is property of info.varonis.com.
Regularly Updating Firmware
The importance of updating your Wi-Fi router’s firmware
Firmware is the software that runs on your Wi-Fi router, and just like any other software, it can have vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Manufacturers often release firmware updates to fix these vulnerabilities and improve the overall security and performance of their routers. Regularly updating your router’s firmware ensures that you have the latest security patches and protection against emerging threats.
How to check for and apply firmware updates
To check for and apply firmware updates on your Wi-Fi router, follow these steps:
- Check for updates: Visit the manufacturer’s website or consult your router’s user manual to find the latest firmware version for your specific router model.
- Access your router’s settings: Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar.
- Enter login credentials: Enter the username and password for your router.
- Navigate to the firmware update settings: Look for the firmware update or system settings section in the router’s settings interface.
- Check for updates: Find the option to check for firmware updates and click on it.
- Apply the update: If a new firmware version is available, follow the instructions to download and apply the update.
- Restart your router: After applying the firmware update, restart your router to ensure the changes take effect.
By regularly updating your router’s firmware, you stay ahead of potential security vulnerabilities and ensure the continued security of your Wi-Fi network.
Using Guest Networks for Smart Security Devices
Why guest networks are beneficial for smart security devices
Guest networks are separate Wi-Fi networks that allow guests to connect to the internet without having access to your main network. Using a guest network for your smart security devices adds an extra layer of security by isolating them from your main network. It prevents potential attackers or unauthorized users from gaining access to your sensitive data or devices.
Steps to set up a guest network on your Wi-Fi router
To set up a guest network on your Wi-Fi router, follow these steps:
- Access your router’s settings: Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar.
- Enter login credentials: Enter the username and password for your router.
- Navigate to the guest network settings: Look for the guest network or wireless settings section in the router’s settings interface.
- Enable the guest network: Turn on the guest network feature.
- Configure the settings: Set a unique name and password for your guest network.
- Set network permissions: Choose the level of access you want to grant to guest network users. It is recommended to restrict access to your smart security devices.
- Save the settings: Save the changes and restart your router if necessary.
By utilizing a guest network for your smart security devices, you maintain the security of your main network while allowing guests to connect to the internet.

This image is property of www.mercku.com.
Securing Smart Security Device Credentials
The significance of strong passwords for smart security devices
Smart security devices often come with default passwords that are widely known or easily guessable. This makes them an easy target for hackers. It is essential to change the default passwords and set strong, unique passwords for each device. Strong passwords significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your devices and the data they hold.
Best practices for managing and securing device credentials
Follow these best practices for managing and securing your smart security device credentials:
- Change default passwords: As soon as you install a smart security device, change the default password to a strong, unique one.
- Use a password manager: Consider using a password manager to securely store and generate strong passwords for your devices.
- Enable two-factor authentication: If your devices support it, enable two-factor authentication for an extra layer of security.
- Regularly update device firmware: Keep your devices updated with the latest firmware to ensure they have the latest security patches.
- Disable unused features: If your devices have unused features or services, disable them to minimize the attack surface.
- Limit access to device controls: Restrict access to device controls by creating separate user accounts with different levels of permissions.
- Educate family members or housemates: Ensure that everyone in your household is aware of the importance of device security and follows best practices for managing device credentials.
By implementing these best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your smart security devices and uphold the overall security of your Wi-Fi network.
Conclusion
In conclusion, securing your Wi-Fi network is paramount to protect your smart security devices from hacking and potential security breaches. By following the best practices discussed in this article, such as choosing a strong Wi-Fi password, enabling network encryption, disabling remote management, changing the default network name, implementing MAC address filtering, regularly updating firmware, using guest networks, and securing smart security device credentials, you can significantly enhance the security of your Wi-Fi network and ensure the protection of your smart security devices. Taking these proactive steps will provide you with peace of mind and the assurance that your home and loved ones remain secure in the digital world.

This image is property of www.kaspersky.com.
